Percona Everest is the first open source, cloud-native platform for automated database provisioning and management. It supports PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and MySQL clusters. It enables multi-database and multi-cluster configurations and can be deployed on any Kubernetes infrastructure in the cloud or on-premises.
Featuring a user-friendly web UI and API for streamlined database and backup management, Percona Everest uses Percona Operators to effortlessly provision database clusters. Developed with Go and cutting-edge tools, it ensures efficiency and reliability.
Let’s look at how Percona Everest manages databases on Kubernetes in a development environment. By deploying Percona Everest directly from the source, you can experience firsthand how it allows you to deploy your database on Kubernetes and treat all environments consistently with a microservices approach.
As a result, you will be able to:
- Discover all the components of Percona Everest.
- Сheck out the latest features that have not been released yet.
- Try to contribute to the code. The dev environment will automatically rebuild Percona Everest with your changes.
Let’s get started.
1. Percona Everest repositories
The source code of the main components of Percona Everest (Frontend, API Server, and everestctl) is placed in one repository. New features are developed in separate branches, but the latest dev version is in the main branch. So, we use the main to start with.
First, create a new directory for the project on your machine and clone the Percona Everest repository there.
git clone [email protected]:percona/everest.git
We also need the Percona Everest operator, so we’ll clone it right away.
git clone [email protected]:percona/everest-operator.git
Now go to the everest directory and on to the dev directory.
cd everest/dev/
This directory contains a Readme.md with detailed instructions on how to start the dev environment and configuration files.
The instructions in Readme.md offer two options for launching:
- locally using k3d;
- in GKE cloud.
In this article, we will use the local environment.
2. Preparing tools
We will run the dev environment locally and create a Kubernetes cluster using k3d (Rancher Lab’s minimal Kubernetes distribution).
Install k3d from the official website. This will also require Docker and kubectl.
Percona Everest uses Tilt.dev for the development workflow. Tilt is a microservices development tool that provides intelligent real-time rebuilding and updating on local servers and Kubernetes.
Install tilt.dev from the official website.
3. Kubernetes cluster creation
Percona Everest with Tilt requires the Artifacts registry. To create a local registry, let’s run the cluster creation command with the parameters.
k3d cluster create everest-dev --registry-create k3d-registry
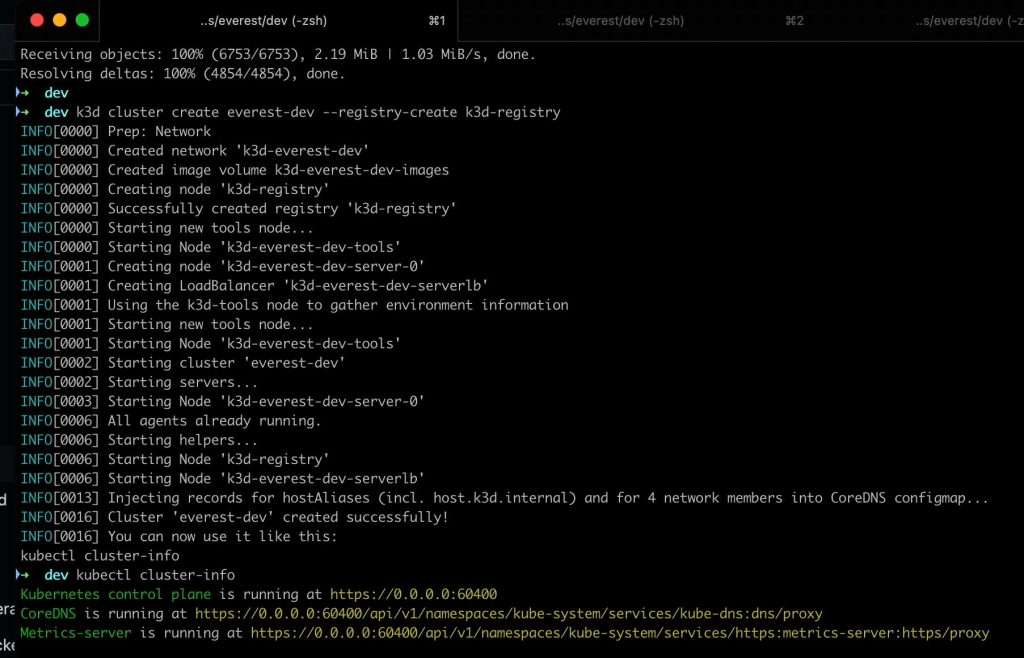
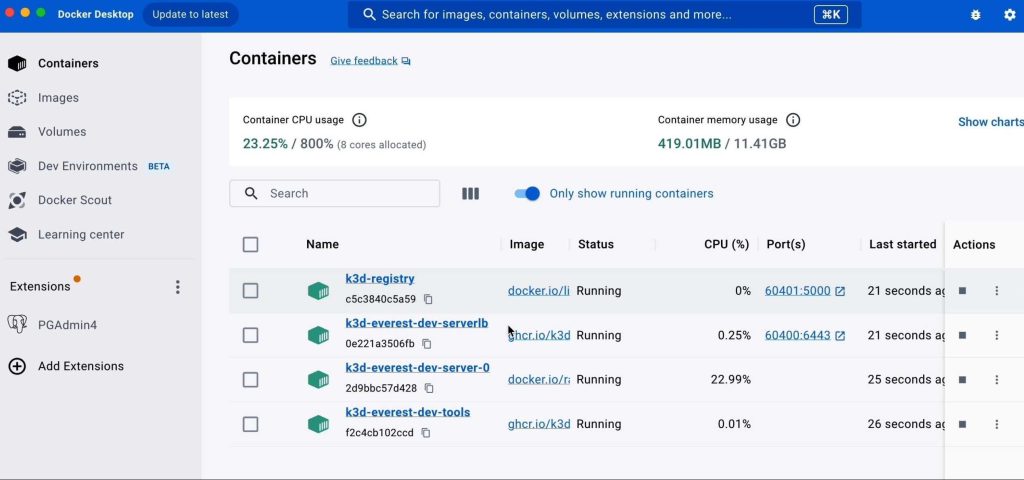
4. Launching Tilt
At the very beginning, we cloned the Percona Everest Operator repository; we will need to specify the path to this repository in an environment variable. Execute the command to set EVEREST_OPERATOR_DIR
export EVEREST_OPERATOR_DIR=/Users/dbazhenov/everest/dev/everest-operator/
Now, open the dev directory in the Everest repository folder, where Tiltfile is located, and run the command to start Tilt.
tilt up
You receive a URL (localhost:10350) to open the Tilt panel in your browser.

Open the Tilt dashboard in your browser and select a resource from the list.
Tilt starts building all the components of Percona Everest, such as the front end, back end, database operators, monitoring tools, and so on. A total of 23 components will be built.
You can switch between components and see the logs.
If errors or warnings occur, restart the component build.
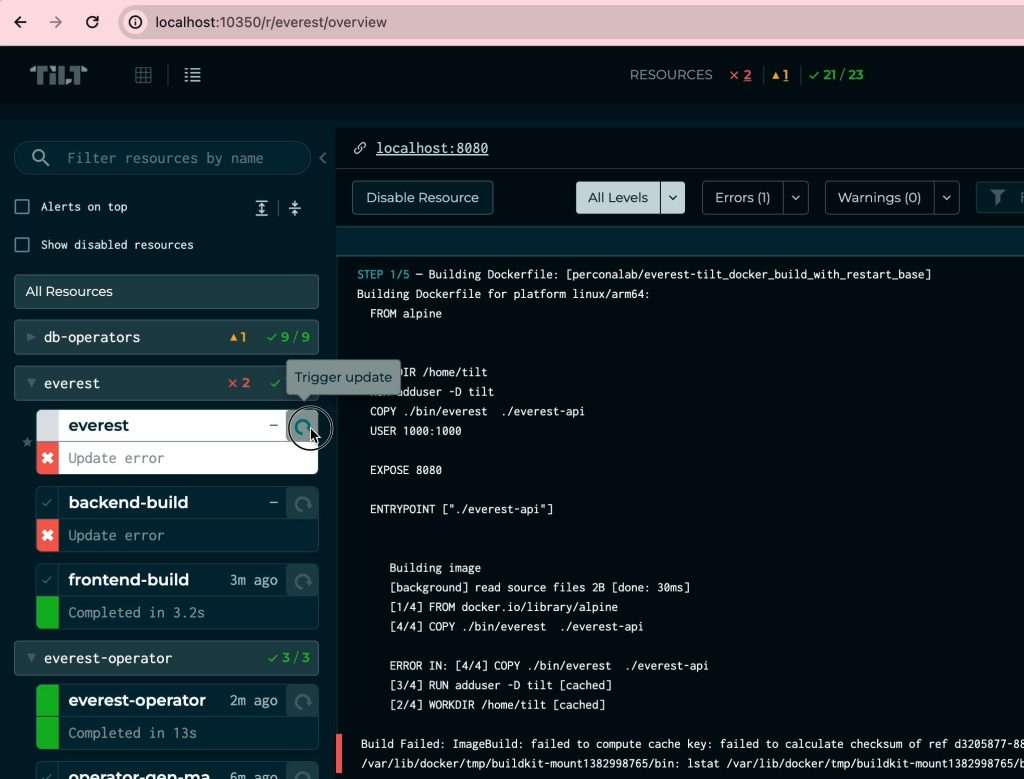
Wait a while until all 23 components have been successfully started.
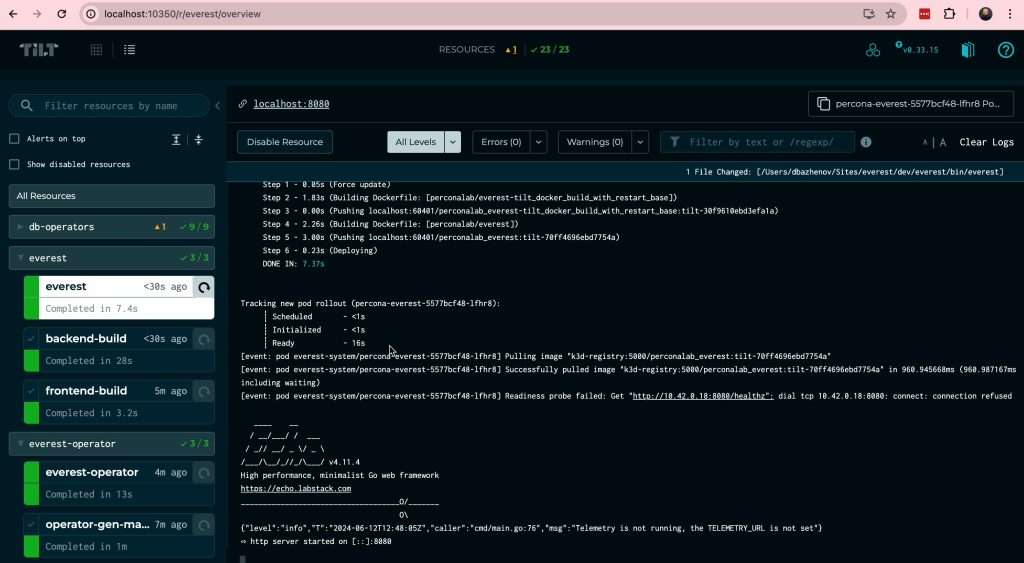
5. Running Percona Everest
When all components are green, you can run Everest in a browser at localhost:8080
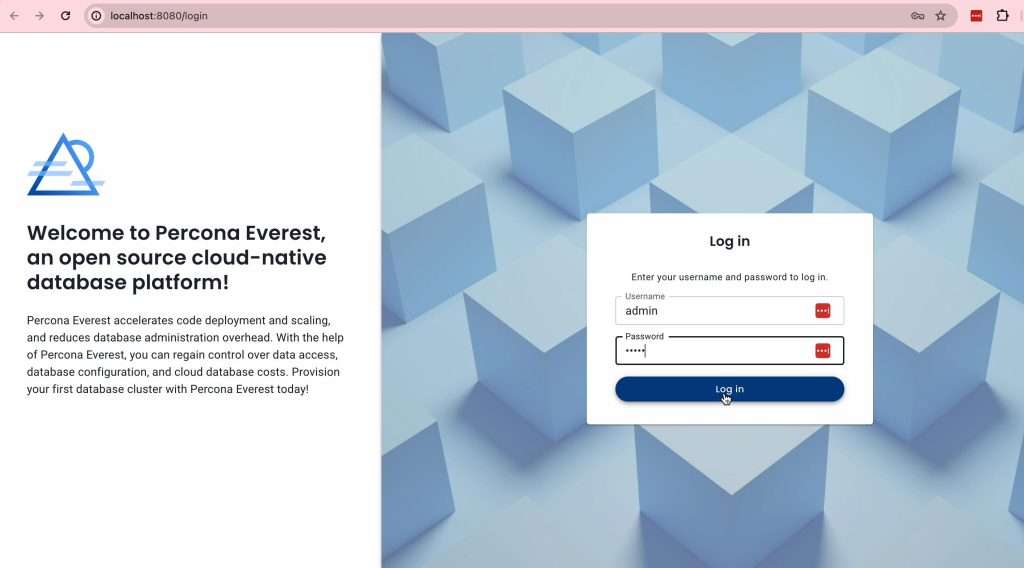
You see the login screen and the new user authentication feature right away. Log in with the user and password, and use admin/admin in a dev environment.
Note that user authentication has not been released at the time of writing this blog post.
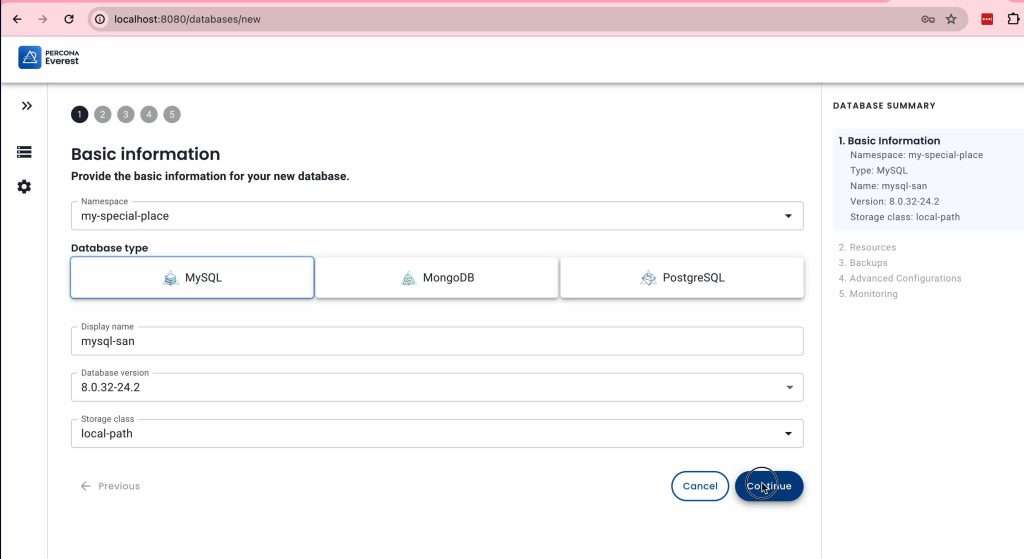
Please share your impressions and suggestions on our forum.
Known issues
If you are using a Mac with ARM processors, you may have problems creating databases in Percona Everest when using a local K3D, Minikube, or Kind cluster. In this case, we recommend using Kubernetes in the cloud. For example, Readme.md contains instructions for running the dev environment in GKE.
Tear down the environment
After completing your experiments, stop the dev environment. Execute commands:
- Tear down tilt
tilt down - Tear down local k8s cluster
k3d cluster delete everest-dev
Conclusion
We ran the dev version of Percona Everest locally in a dev environment from the source code repository.
Percona Everest helps to transform your database infrastructure into an automated private DBaaS, eliminating vendor lock-in and complex in-house development.
The main branch contains the latest changes, and you can always test new features that will be published in the next release. Update the main branch periodically. You can also experiment with modifying the code. When you change any files, Tilt will automatically track the changes and do a rebuild. You will see your changes in your local Percona Everest.
We would be very grateful for your feedback! Please create a new topic in the forum or issue in GitHub and let us know your impressions from running Percona Everest or any problems you find.






