This blog was first authored by Pete Scott in 2023. We’ve updated it in 2025 for clarity and relevance, reflecting current practices while honoring their original perspective.
If you’re hearing more about PostgreSQL these days, you’re not alone. Maybe your team is considering it for a new project, or you’re seeing it pop up everywhere and want to know why. PostgreSQL has been around for more than 25 years, but right now, it’s at the center of conversations about data and scale, powering everything from small businesses to the world’s largest platforms.
You might be wondering: what sets PostgreSQL apart? Why is it getting so much attention from developers and enterprises alike? And is it the right fit for your needs? Let’s explore what PostgreSQL can do, what makes it unique, and what you need to keep in mind if you’re thinking about using it.
What is PostgreSQL?
If you need a database that can grow with your ideas and keep your data safe, PostgreSQL is worth a close look. It’s a powerful, open source object-relational database that’s built to handle just about anything: complex data types, detailed queries, and all the relationships that matter to your business.
PostgreSQL is highly expandable, allowing users to add new functions, data types, and other features. Its strong compliance with SQL standards, combined with support for ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties, makes it an ideal choice for developers and enterprises looking for a scalable, efficient, and secure database.
Why use PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL gives you a level of flexibility that’s hard to match. If you need to store everything from traditional relational data to JSON, geometric shapes, or custom data types, PostgreSQL can handle it all in one place, no extra workarounds or multiple databases required. You’re free to shape your database to fit your project, not the other way around.
As your needs change, PostgreSQL keeps up. You can add your own functions, operators, and data types, so your database grows right along with your business. Because it’s open source, you’re never limited by someone else’s roadmap or licensing rules.
And you’re not on your own. There’s a huge community behind PostgreSQL, ready to help when you need it. Whether you’re searching the documentation, asking a question in the forums, or looking for the latest updates, there’s always support at your fingertips. Problems get solved, best practices are shared, and improvements keep rolling in, so you’re never left behind.
What are the benefits of PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL’s benefits read like a database administrator’s wish list. But understanding these benefits in the context of real-world enterprise challenges is crucial.
Flexibility and extensibility
With PostgreSQL, you’re in control. You can customize almost every aspect: choose your programming language, define your own data types, and create the functions that matter for your projects. Instead of working around limitations, you can solve problems directly in the database and shape it to fit whatever you’re building.
Performance and scalability
PostgreSQL excels at performance and scalability, easily handling large amounts of data and concurrent transactions. It uses complex optimization techniques to ensure efficient data storage and retrieval, making it appropriate for high-demand settings. Features like horizontal scaling, partitioning, and replication let you expand when you need to, so you don’t have to worry about hitting a wall as you scale.
Robust transaction support
You need data you can count on. PostgreSQL delivers full ACID compliance and multiple transaction isolation levels, so your information stays consistent and safe, even in complex, multi-user environments.
Advanced query optimization
PostgreSQL’s extensive query optimization capabilities enable the efficient execution of complex queries. It contains capabilities such as index-only scans, bitmap heap scans, and genetic query optimization to reduce query execution times. This makes PostgreSQL ideal for data analysis and business intelligence applications requiring fast and accurate data retrieval.
Active community and ecosystem
The active community and ecosystem around PostgreSQL greatly contribute to its strength and utility, as a network of developers, users, and organizations drives its continuous improvement, bolstering its security and support structures. This community offers a range of plugins, tools, extensions, documentation, and forums.
What’s behind PostgreSQL’s meteoric rise in popularity and usage?
PostgreSQL hasn’t just been a concern to its competitors; it’s swooped past most of them.
StackOverflow statistics show that 26% of developers preferred it in 2017, 34% in 2019, and 40% in 2021. Most recently, in StackOverflow’s 2024 Stack Developer Survey, PostgreSQL extended its lead over MySQL (48.7% to 40.3%) as the most popular database platform among professional developers.
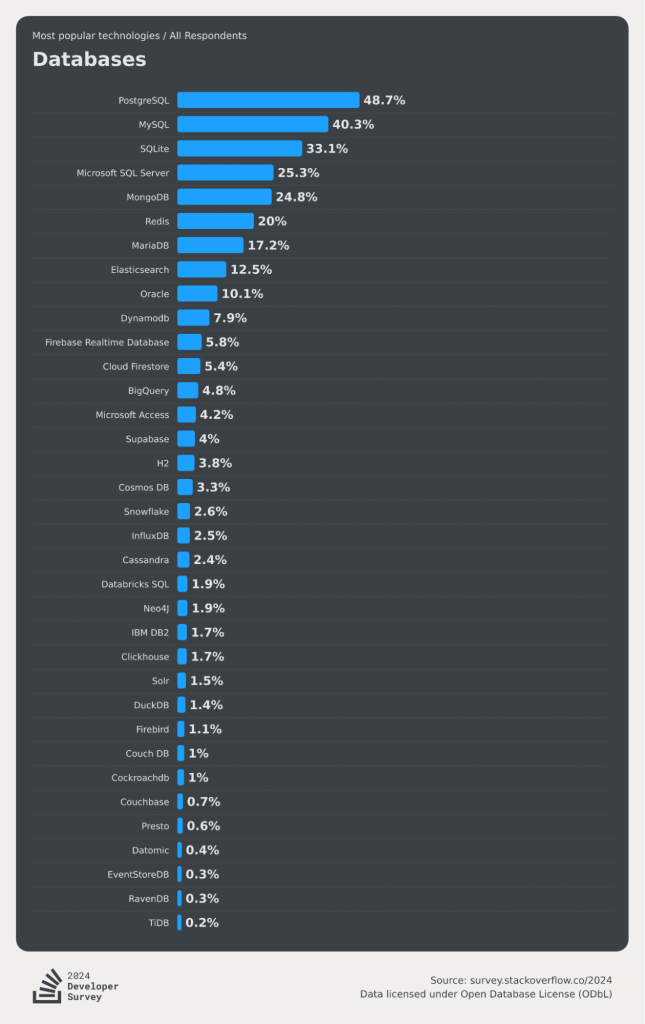
In another survey, using multiple metrics for overall popularity, PostgreSQL ranks as the fourth most popular database management system (DB-Engines, June 2025).
The widespread use and popularity have come on like gangbusters in recent years, but PostgreSQL wasn’t always the cool kid. It has evolved steadily, however, during 25 years as an open source project. (Craig Kerstiens, crunchydata)
That evolution has created lots of reasons for its expanding popularity. PostgreSQL has powerful and advanced features, including asynchronous replication, full-text searches of the database, and native support for JSON-style storage, key-value storage, and XML. PostgreSQL is also highly extensible, enabling users to add custom functionality through plug-ins and extensions.
Another reason for PostgreSQL’s popularity (perhaps the biggest) is that it’s open source and free to use, distribute, and modify. Anyone can use it for private, commercial, or academic purposes.
And there’s a global community dedicated to keeping it open source. People from every corner of tech contribute their expertise, share solutions, and review the code together, so issues get spotted quickly, best practices spread fast, and the software keeps getting better.
More on PostgreSQL security and reliability
These days, PostgreSQL security is top of mind for many teams, and with the right setup, you get advanced, proven features: internal authentication, external server-based authentication, SSL encryption, data encryption at rest, and the ability to define custom roles and permissions for users.
Reliability is yet another factor in the PostgreSQL popularity upswing. Here are the elements that form the backbone of that reliability:
- PostgreSQL has a robust transactional system that ensures data integrity and consistency, even in high-transaction environments.
- A multi-version concurrency control (MVCC) system ensures multiple users can access the same data simultaneously without conflicts or data loss.
- It’s well-suited for organizations that require mission-critical applications with high availability. PostgreSQL supports multiple concurrent users and can handle complex database operations without downtime or data loss.
- PostgreSQL is ACID-compliant, which means it meets the principles of atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability — the key properties of a reliable database system.
On-demand webinar: PostgreSQL security missteps and tips
PostgreSQL vs. MySQL: What are the key differences and similarities?
 The aforementioned attributes explain why many are turning to PostgreSQL, but why do users go with PostgreSQL instead of MySQL (which edges out PostgreSQL for simplicity and ease-of-use)? Here are potential reasons:
The aforementioned attributes explain why many are turning to PostgreSQL, but why do users go with PostgreSQL instead of MySQL (which edges out PostgreSQL for simplicity and ease-of-use)? Here are potential reasons:
- PostgreSQL offers advanced SQL features, including support for complex queries, window functions, common table expressions (CTEs), and more.
- PostgreSQL has more advanced data integrity features and constraints, allowing for finer control over data validation and enforcement of business rules.
- PostgreSQL has superior support for JSON data types, making it a good choice for applications requiring structured and semistructured data.
- PostgreSQL has advanced support for geospatial data and geographic information system (GIS) functionality, making it a preferred choice for applications that deal with location-based data.
- PostgreSQL is released under the PostgreSQL License, which is more permissive than MySQL’s dual licensing (GPL or commercial).
Differences
While both PostgreSQL and MySQL are widely used relational database management systems, they each have unique characteristics that distinguish them, such as:
- Licensing: PostgreSQL is distributed under the PostgreSQL License, a permissive open source license. In contrast, MySQL offers dual licensing options: the GNU General Public License (GPL) for open-source projects and a proprietary commercial license for other uses.
- Data types: PostgreSQL provides a more extensive selection of data types than MySQL, encompassing complex types such as arrays, JSON, XML, and user-defined types, allowing for more flexibility in data storage and manipulation.
- SQL syntax and features: Although both databases utilize SQL for querying, there are notable distinctions in their SQL syntax and capabilities. PostgreSQL, for instance, includes support for window functions, Common Table Expressions (CTEs), and recursive queries, areas where MySQL might offer limited functionality.
- Transaction isolation levels: PostgreSQL offers a broader array of transaction isolation levels, including the highly stringent Serializable level, providing more options for controlling concurrency and data integrity.
- Performance and scaling: PostgreSQL stands out for its strong performance and scalability, especially with complex queries and large datasets. While MySQL has traditionally excelled in simple, read-heavy operations, both systems have evolved to enhance their performance capabilities over time.
Similarities
Although PostgreSQL and MySQL have their unique characteristics, they also share several key features that underline their core functionalities:
- Both are Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS): Both PostgreSQL and MySQL fall under the category of relational database systems, organizing data into structured tables of rows and columns, and leveraging SQL for data manipulation and queries.
- ACID compliance: Each database system upholds ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) principles, providing a foundation for secure and reliable transaction processing.
- Cross-platform compatibility: PostgreSQL and MySQL are designed to operate across multiple operating systems, including Linux, Windows, and macOS, offering flexibility in deployment environments.
- Community support: Both databases benefit from active, supportive communities that contribute to ongoing development, provide support, and offer resources for users.
- Support for replication and high availability: To ensure continuous operation and data safety, both PostgreSQL and MySQL incorporate mechanisms for data replication and high availability to ensure data redundancy and fault tolerance in distributed systems.
What is PostgreSQL used for? Exploring common use cases

These days, PostgreSQL is used for a lot of high-stakes purposes and by a lot of companies.
General PostgreSQL use cases
In addition to being used as a backend database management system, here are other general uses of PostgreSQL software:
Website applications: Because PostgreSQL can handle high volumes of data and concurrent users efficiently, it’s suitable for applications that require scalability and performance. This makes it an excellent choice for dynamic website applications, from e-commerce platforms to content management systems, where uptime and data integrity are critical.
Geographic information systems (GIS): PostgreSQL is often preferred for mapping and related services because of its advanced support for geospatial data. The PostGIS extension, in particular, enhances PostgreSQL, making it one of the most powerful databases for managing GIS data, supporting complex queries, and spatial analyses essential for geographic and location-based services.
Data warehousing: PostgreSQL enables businesses to store and analyze large amounts of data for reporting and business intelligence. Its capability to handle massive datasets and complex queries and its support for advanced data types make it ideal for integrating and consolidating data from various sources for comprehensive analysis.
Data analytics: PostgreSQL can support analytical processing and reporting with the right extensions and configurations. This adaptability allows for the implementation of data mining techniques and predictive analytics, providing valuable insights that can inform business strategies and decision-making processes.
Social media platforms: Companies use PostgreSQL to manage user profiles, posts, connections, and interactions. Its ability to efficiently manage large relational datasets and handle many transactions makes it ideal for the fast-paced and data-heavy demands of social media applications.
Industry-specific PostgreSQL use cases
Businesses and organizations across industries use PostgreSQL. Industry-specific uses include:
E-commerce: PostgreSQL helps online retailers manage product catalogs, customer data, orders, and transactions without missing a beat. Its reliability and ability to scale support fast-changing inventory and high transaction volumes, giving customers a smoother shopping experience and keeping operations running efficiently.
Financial institutions: Because it’s ACID-compliant, PostgreSQL streamlines and safeguards transaction handling in financial systems and online banking. Its security features and ability to handle complex financial data make it a trusted choice for managing sensitive financial transactions and customer information.
Science and research companies: PostgreSQL is a favorite for storing and analyzing experimental results, research data, and other complex datasets. Its support for advanced data types and powerful queries makes it easier for scientists to handle large projects and deep analysis.
Healthcare organizations: Patient records, medical histories, and clinical data require careful handling. PostgreSQL delivers the data integrity and security healthcare providers count on to keep information confidential and reliable, helping them meet strict privacy and compliance requirements.
Government: Public agencies use PostgreSQL for everything from voter registration to managing public records and administrative databases. Its reliability and flexibility help governments keep essential information accessible, secure, and organized.
Educational institutions: Universities and schools use PostgreSQL to organize student information, schedules, and academic records. Its ability to adapt supports the varied data management needs of education, from small classrooms to sprawling campuses.
Telecommunications: Real-time data processing is crucial for telecom providers. PostgreSQL supports billing, call records, and subscriber management with the speed and reliability needed to keep customers connected and businesses running smoothly.
Building on that solid foundation: Is PostgreSQL enterprise-ready?
Now it’s time to go more in-depth on the final question: Is it enterprise-ready?
There’s no doubt PostgreSQL provides a solid foundation for innovative development. It’s reliable, robust, feature-rich, and performant. Unfortunately, in its vanilla form, PostgreSQL does not have all the components needed to create large-scale, complex systems and applications that meet the needs of enterprise businesses and organizations.
You could try to cover enterprise production requirements by choosing a proprietary PostgreSQL fork. But then you’re beholden to a single vendor who can lock you in. Licensing can be expensive, and you may find your ability to innovate limited by someone else’s roadmap.
Knowing that, you might try the do-it-yourself route with open source tools and extensions. Making PostgreSQL work across the enterprise means adding high availability, disaster recovery, monitoring, observability, and more, then configuring and testing these pieces to work together. This approach adds significant complexity to your IT team’s responsibilities and requires deep expertise to maintain peak performance as you grow. Over time, these challenges can pile up.
Get enterprise-grade PostgreSQL without compromise
If you’re considering your next move, now is the time to look past the surface and see the trade-offs of both DIY and proprietary options for running PostgreSQL in the enterprise. We’ve put together a comprehensive resource center on the real costs and day-to-day burdens, covering everything from ongoing maintenance, troubleshooting, and hiring to the operational slowdowns and resource strain that can creep in as your environment grows. See what it really takes to manage PostgreSQL at scale, and discover how you can keep control and stay flexible for the long term.
Discover the real cost of managing PostgreSQL in-house and how Percona helps you avoid the headaches.
FAQs
1. What is Postgres used for, and how does it differ from other database management systems?
PostgreSQL is an advanced, open source object-relational database management system (ORDBMS) known for its robustness, extensibility, and SQL standards adherence. It stands out from other databases with its support for advanced data types, comprehensive transaction integrity (ACID compliance), and the ability to extend functionality through user-defined types and functions.
2. Is PostgreSQL suitable for small-scale projects or only for enterprise-level applications?
PostgreSQL is highly versatile and can be used for both small-scale projects and enterprise-level applications. Its scalability, combined with a rich set of features and the ability to handle large volumes of data and concurrent transactions, makes it suitable for projects of any size.
3. What are some common use cases for PostgreSQL in business and development?
PostgreSQL serves a wide range of applications across different industries, from managing inventory and transactions on e-commerce sites and ensuring secure, ACID-compliant processes in financial systems to handling spatial data in GIS and supporting data warehousing and analytics for insightful business intelligence. Its adaptability also makes it ideal for web and mobile application development, content management, and handling user data on social media platforms, among other uses.
4. Is PostgreSQL suitable for cloud-based deployments?
Yes, PostgreSQL is well-suited for cloud-based deployments. Its compatibility with various cloud platforms and services allows for scalable, resilient, and flexible database solutions in the cloud.







