Take Back Control of your Cloud Databases
How to cut costs, accelerate releases, support AI workloads, and stay portable with cloud-native Kubernetes databases.

Take Back Control of Your Cloud Databases
How to cut costs, accelerate releases, support AI workloads, and stay portable with cloud-native Kubernetes databases.

The case for running your databases on Kubernetes
Modern cloud-native architectures have enabled organizations to build, deploy, and scale applications with unprecedented speed. Teams can release new features rapidly, adapt to shifting business demands, and scale dynamically to meet traffic surges.
Yet most enterprises are still slowed by the past.
While applications modernized, databases largely did not. Many remain tied to legacy operational models or expensive proprietary Database-as-a-Service platforms that create delays, operational silos, and unpredictable costs that escalate as business grows. These challenges undermine cloud agility and force teams to trade innovation for risk avoidance.
AI is amplifying the strain. As infrastructure for AI inference and training expands, costs for continuously running workloads rise sharply. When the unit cost of operating AI in the public cloud approaches the cost of dedicated infrastructure, financial leaders shift toward models that restore control of data, performance, and spend. How the database tier is operated becomes a critical part of that shift.
The most common challenges fall into three categories.

Provisioning delays
Teams face bottlenecks that slow developer velocity.
-
- Requests turn into tickets, tickets turn into queues
- Databases scale slower than microservices around them
- Hand-offs create opportunities for configuration drift and incident risk
Every delayed database results in a delayed feature — and a delayed revenue opportunity.

Opaque and rising cloud database costs
The financial impact compounds as cloud footprints expand.
-
- Markups nest inside proprietary services
- Scaling often requires jumping to larger, more expensive tiers
- Multi-region replication and data movement carry significant premiums
Predictability erodes just as data becomes more central to growth.

Fragmented governance and lock-in risks
Database decisions shape future architectural freedom.
-
- Data residency and compliance enforcement differ across systems
- Each DBaaS introduces new operational boundaries and tooling
- Exiting a provider requires costly rewrites and migration window risk
Short-term convenience transforms into long-term constraint.
These challenges build over time, resulting in complexity, cost inefficiency, and a growing drag on strategic execution.
A modern cloud operating model is emerging that aligns the database tier with the speed and automation of cloud-native application platforms: open source databases orchestrated by Kubernetes.
How modernization removes operational and financial constraints
Databases on kubernetes provide a unified operational approach that applies the same automation, pipelines, observability, and security—already standard for application workloads—to the data tier.
Three benefits stand out:
1. Cloud spend under control
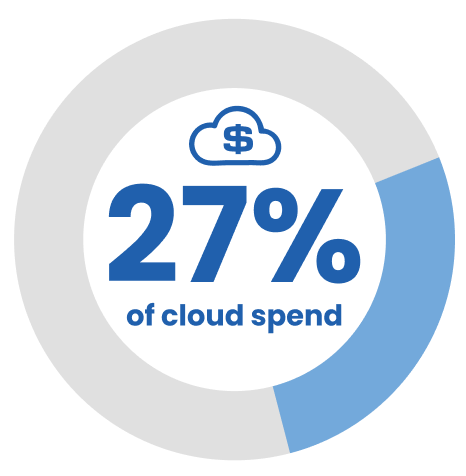
Organizations waste an estimated 27% of cloud spend through idle or oversized capacity. Eliminating DBaaS markups on compute, storage, replication, and backups materially reduces overspend. Direct infrastructure costs can decrease by 30–50% for production workloads, with more predictable scaling and regional expansion.
For a personalized estimate of your potential savings, the full report includes access to our TCO pricing calculator.
2. Faster database delivery and higher developer velocity
When databases live on the same platform as applications:

Provisioning happens in minutes, not weeks

Developers work through GitOps and existing CI/CD workflows

Platform friction no longer slows launch cycles
3. Freedom of architecture and movement
With portability across clouds and on-prem environments:
-
- Data stays close to AI workloads to reduce latency and cost
- Multi-cloud architecture becomes practical, not theoretical
- Pricing changes and licensing shifts no longer dictate strategy
Where organizations stand today
Adoption data shows the industry is mid-transition.
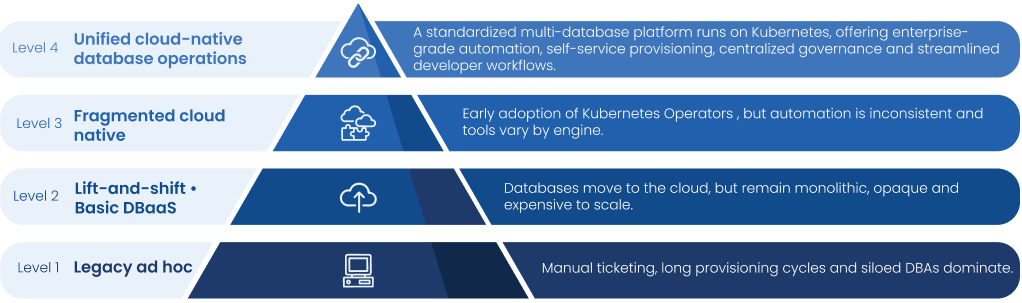
Most enterprises have lifted databases into the cloud but continue operating them through legacy delivery and control models. A smaller group has begun running databases on Kubernetes but with inconsistent automation and tooling across different engines, creating fragmentation instead of standardization.
The gap between cloud-native aspirations and database operations widens with scale:
-
- Provisioning delays ripple across roadmap timelines
- Cloud bills rise faster than revenue
- Security and compliance teams manage more perimeters with less visibility
- Specialized database teams struggle to support more services
AI changing the economics
Pressure on AI infrastructure spend is accelerating database modernization.
Running AI inference on public cloud GPU instances for long periods often exceeds the cost of controlled infrastructure alternatives. When inference operates at scale, keeping data and compute together becomes financially mandatory.
Unifying AI-adjacent databases on a portable platform helps enterprises:
-
- Avoid unnecessary egress charges
- Improve data governance for sensitive training data
- Maintain mobility as needs shift between clouds and on-prem
Technology leaders increasingly evaluate cloud deployment strategies through the lens of unit economics, not convenience.
A better operating model for the cloud database tier
A standardized approach to managing data services on Kubernetes provides the operational consistency enterprises require to scale:
-
- Shared automation for provisioning, HA, scaling, upgrades, and failover
- One security and governance framework applied universally
- A single platform engineering model that scales talent, not silos
- Predictable financial planning grounded in real resource usage
This model is emerging as the foundation for long-term database agility in the cloud.

Take Back Control of Your Cloud Databases
Cloud agility cannot reach its full potential until databases modernize alongside applications. Standardizing database operations on Kubernetes reconnects business innovation with the data systems that power it, enabling faster delivery, predictable cost, and architectural freedom at scale.
Download the full report to explore modernization benchmarks, detailed TCO modeling, and a practical roadmap for transitioning the data tier to a cloud-native operating model.
Related Content: Your Kubernetes Database Resources
Explore these essential resources for deeper insights into cost, architecture, and more.
Strategic Trade-Offs: Compare managed database vs Kubernetes head-to-head to weigh the impact on cost predictability, vendor lock-in, agility, and long-term control.
Architectural Control: Learn how Kubernetes multi-cloud architecture allows you to execute a strong multi-cloud strategy that cuts costs and strengthens resilience by building portable databases without vendor dependence.
Choosing the Right Operator: Get an in-depth comparison of the various Kubernetes Operators on the market.
Team Performance: Discover how embracing a Kubernetes data platform helps improve developer velocity by enabling self-service provisioning and faster release cycles.
Financial Tool: Access our TCO Pricing Calculator to move beyond conceptual savings and create a personalized estimate of your potential financial benefits.
Prefer to Listen? Listen to this edition to Open Source Unplugged on how Kubernetes is a game change for platform development.
The case for running your databases on Kubernetes
Modern cloud-native architectures have enabled organizations to build, deploy, and scale applications with unprecedented speed. Teams can release new features rapidly, adapt to shifting business demands, and scale dynamically to meet traffic surges.
Yet most enterprises are still slowed by the past.
While applications modernized, databases largely did not. Many remain tied to legacy operational models or expensive proprietary Database-as-a-Service platforms that create delays, operational silos, and unpredictable costs that escalate as business grows. These challenges undermine cloud agility and force teams to trade innovation for risk avoidance.
AI is amplifying the strain. As infrastructure for AI inference and training expands, costs for continuously running workloads rise sharply. When the unit cost of operating AI in the public cloud approaches the cost of dedicated infrastructure, financial leaders shift toward models that restore control of data, performance, and spend. How the database tier is operated becomes a critical part of that shift.
The most common challenges fall into three categories.

Provisioning delays
Teams face bottlenecks that slow developer velocity.
- Requests turn into tickets, tickets turn into queues
- Databases scale slower than microservices around them
- Hand-offs create opportunities for configuration drift and incident risk
Every delayed database results in a delayed feature — and a delayed revenue opportunity.

Opaque and rising cloud database costs
The financial impact compounds as cloud footprints expand.
- Markups nest inside proprietary services
- Scaling often requires jumping to larger, more expensive tiers
- Multi-region replication and data movement carry significant premiums
Predictability erodes just as data becomes more central to growth.

Fragmented governance and lock-in risks
Database decisions shape future architectural freedom.
- Data residency and compliance enforcement differ across systems
- Each DBaaS introduces new operational boundaries and tooling
- Exiting a provider requires costly rewrites and migration window risk
Short-term convenience transforms into long-term constraint.
These challenges build over time, resulting in complexity, cost inefficiency, and a growing drag on strategic execution.
A modern cloud operating model is emerging that aligns the database tier with the speed and automation of cloud-native application platforms: open source databases orchestrated by Kubernetes.
How modernization removes operational and financial constraints
Databases on kubernetes provide a unified operational approach that applies the same automation, pipelines, observability, and security—already standard for application workloads—to the data tier.
Three benefits stand out:
1. Cloud spend under control

Organizations waste an estimated 27% of cloud spend through idle or oversized capacity. Eliminating DBaaS markups on compute, storage, replication, and backups materially reduces overspend. Direct infrastructure costs can decrease by 30–50% for production workloads, with more predictable scaling and regional expansion.
For a personalized estimate of your potential savings, the full report includes access to our TCO pricing calculator.
2. Faster database delivery and higher developer velocity
When databases live on the same platform as applications:

Provisioning happens in minutes, not weeks

Developers work through GitOps and existing CI/CD workflows

Platform friction no longer slows launch cycles
3. Freedom of architecture and movement
With portability across clouds and on-prem environments:
-
- Data stays close to AI workloads to reduce latency and cost
- Multi-cloud architecture becomes practical, not theoretical
- Pricing changes and licensing shifts no longer dictate strategy
Where organizations stand today
Adoption data shows the industry is mid-transition.
Most enterprises have lifted databases into the cloud but continue operating them through legacy delivery and control models. A smaller group has begun running databases on Kubernetes but with inconsistent automation and tooling across different engines, creating fragmentation instead of standardization.
The gap between cloud-native aspirations and database operations widens with scale:
-
- Provisioning delays ripple across roadmap timelines
- Cloud bills rise faster than revenue
- Security and compliance teams manage more perimeters with less visibility
- Specialized database teams struggle to support more services

AI changing the economics
Pressure on AI infrastructure spend is accelerating database modernization.
Running AI inference on public cloud GPU instances for long periods often exceeds the cost of controlled infrastructure alternatives. When inference operates at scale, keeping data and compute together becomes financially mandatory.
Unifying AI-adjacent databases on a portable platform helps enterprises:
-
- Avoid unnecessary egress charges
- Improve data governance for sensitive training data
- Maintain mobility as needs shift between clouds and on-prem
Technology leaders increasingly evaluate cloud deployment strategies through the lens of unit economics, not convenience.
A better operating model for the cloud database tier
A standardized approach to managing data services on Kubernetes provides the operational consistency enterprises require to scale:
-
- Shared automation for provisioning, HA, scaling, upgrades, and failover
- One security and governance framework applied universally
- A single platform engineering model that scales talent, not silos
- Predictable financial planning grounded in real resource usage
This model is emerging as the foundation for long-term database agility in the cloud.

Take Back Control of Your Cloud Databases
Cloud agility cannot reach its full potential until databases modernize alongside applications. Standardizing database operations on Kubernetes reconnects business innovation with the data systems that power it, enabling faster delivery, predictable cost, and architectural freedom at scale.
Download the full report to explore modernization benchmarks, detailed TCO modeling, and a practical roadmap for transitioning the data tier to a cloud-native operating model.
Related Content: Your Kubernetes Database Resources
Explore these essential resources for deeper insights into cost, architecture, and more.
Strategic Trade-Offs: Compare managed database vs Kubernetes head-to-head to weigh the impact on cost predictability, vendor lock-in, agility, and long-term control.
Architectural Control: Learn how Kubernetes multi-cloud architecture allows you to execute a strong multi-cloud strategy that cuts costs and strengthens resilience by building portable databases without vendor dependence.
Choosing the Right Operator: Get an in-depth comparison of the various Kubernetes Operators on the market.
Team Performance: Discover how embracing a Kubernetes data platform helps improve developer velocity by enabling self-service provisioning and faster release cycles.
Financial Tool: Access our TCO Pricing Calculator to move beyond conceptual savings and create a personalized estimate of your potential financial benefits.
Prefer to Listen? Listen to this edition to Open Source Unplugged on how Kubernetes is a game change for platform development.